

The aim of this study was to determine if the physiological dead space in prematurely born infants with RDS or evolving/established bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) was greater than in term controls with no respiratory disease.
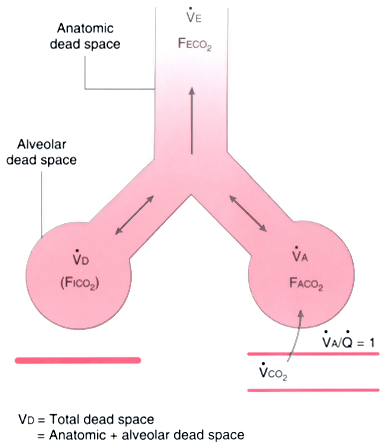
10 A previous study has shown that a reduction in alveolar ventilation resulted in hypercapnia in ventilated infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). In contrast, knowledge of the alveolar ventilation (the volume of air that reaches the alveoli per minute) provides information on the volume of gas taking part in gas exchange at the alveolar–capillary interface. Minute ventilation fails to adequately describe ventilation efficiency as it does not differentiate between alveolar (effective) and dead space ventilation. 6 In pulmonary diseases in infants, there are a variety of pathologies and hence the dead space is not predictable and has rarely been reported. Alveolar dead space comprises alveoli which are ventilated, but not supplied by the pulmonary arterial circulation, or alveoli which are atelectatic. The anatomical dead space is the total volume of the conducting airways from the nose or mouth to the terminal bronchioles, and in ventilated infants includes the apparatus dead space (endotracheal tube and flow sensor). The physiological dead space is the anatomical dead space plus alveolar dead space. 4, 5Īn important influence on the appropriate size of the delivered volume during mechanical ventilation is the size of the dead space, the volume of inhaled gas that does not take part in gas exchange. 3 Inappropriately small tidal volumes can be associated with a prolonged duration of mechanical ventilation, a pro-inflammatory state and an increased work of breathing. 2 Delivery of inappropriately large tidal volumes can lead to alveolar over-distension and development of chronic respiratory morbidity. 1 Use of volume-targeted ventilation is a lung protective strategy as it potentially avoids too high or too low delivered volumes.
Newborn infants often require respiratory support with invasive mechanical ventilation, unfortunately such infants can develop chronic respiratory morbidity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
